Introduction
Proton Trade Layer (PEM) electrolyzers are key parts in the creation of green hydrogen, a spotless and maintainable energy transporter. Understanding the parts of a PEM electrolyzer is fundamental for handle the way this functions and its job in the progress to clean energy. This thorough aide expects to demystify the different parts of a PEM electrolyzer, making sense of their capabilities and importance in the hydrogen creation process.
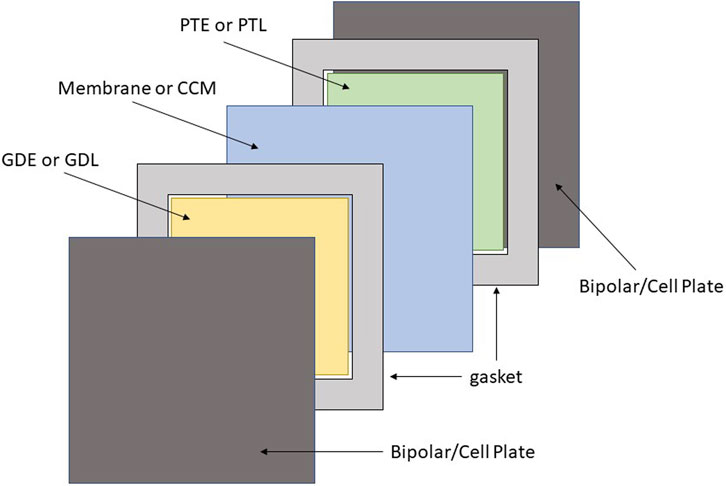
The Core Components
A pem electrolysis comprises a few fundamental parts that cooperate to part water (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) through electrolysis. How about we investigate these parts exhaustively:
- Anode
- Function:The anode is the cathode where the oxidation half-response happens. At the anode, water particles are parted into oxygen, protons (hydrogen particles), and electrons.
- Material: Regularly made of a conductive material like platinum or different impetuses to work with the response.
- Cathode
- Function: The cathode is the terminal where the decrease half-response happens. Here, protons and electrons consolidate to shape hydrogen gas.
- Material: Like the anode, the cathode is additionally made of impetus materials, frequently platinum-based.
- Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM)
- Function: The PEM is a strong polymer electrolyte that isolates the anode and cathode compartments. It permits the entry of protons (H+ particles) while hindering the development of electrons. This specific penetrability is significant for the electrolysis interaction.
- Material: PEMs are normally made of particular polymer materials, like Nafion or other perfluorosulfonic acids.
- Bipolar Plates
- Function: Bipolar plates are utilized to circulate reactants (water and particles) to the anode surfaces and gather the delivered gases (hydrogen and oxygen). They additionally offer primary help to the cell stack.
- Material: Bipolar plates are frequently made of conductive materials like graphite or covered metals.
- Gaskets and Seals
- Function: Gaskets and seals guarantee that the electrolyte compartments are fixed firmly to forestall gas releases and keep up with the respectability of the cell.
- Material: These parts are regularly made of elastomers or different materials impervious to substance responses.
- Current Collectors
- Function: Flow authorities work with the progression of power created during electrolysis. They gather electrons from the cathodes and move them to an outer circuit.
- Material: Current authorities are typically made of conductive materials like graphite or metals.
- Cooling System
- Function: In bigger PEM electrolyzer frameworks, cooling frameworks are utilized to disseminate heat created during the electrolysis cycle, keeping up with the working temperature inside a reasonable reach.
- Components: Cooling frameworks might incorporate intensity exchangers, siphons, and radiators.
The Electrolysis Process
Understanding the parts of a PEM electrolyzer is urgent for fathoming the electrolysis interaction:
Water is provided to the anode compartment.
An electrical momentum is applied, making water particles split into oxygen, protons (H+ particles), and electrons at the anode.
The protons relocate through the PEM to the cathode compartment, while electrons travel through an outer circuit.
At the cathode, protons and electrons join to shape hydrogen gas.
Oxygen is delivered at the anode as a result.
Conclusion
The parts of a PEM electrolyzer work as one to other work with the spotless and effective creation of hydrogen through water electrolysis. Understanding these parts and their capabilities is fundamental for tackling the capability of green hydrogen as a perfect energy transporter and a central member in the change to an economical energy future.